
PowerShell and Windows PowerShell
PowerShell and Windows PowerShell
Quickstart
# Check your version
$PSVersionTable.PSVersion
# Install or update PowerShell
winget install --id Microsoft.PowerShell --source winget
winget upgrade Microsoft.PowerShell
# Launch PowerShell 7
pwsh
Above, from where does pwsh comes from?
pwsh is the executable name for PowerShell 7 and later. It stands for:
PowerShell → pwsh
On Windows PowerShell 5.1, the executable was powershell.exe
But since PowerShell 7 is cross-platform (Windows, Linux, macOS), the new, shorter command works everywhere:
pwsh
So when you see pwsh, just remember:
- It is the modern, open-source, cross-platform version of PowerShell.
- It’s the one you should launch for any new script or automation.
Current situation
Here I suppose you have a recent Windows 11 (version above 22H2 that comes with Terminal Windows)
There are 2 versions of PowerShell available
- Windows PowerShell (5.1 for example)
- Windows PowerShell is specific to Windows, it is NOT portable, hence the name: Windows PowerShell
- Comes with Windows
- Path to the app:
%SystemRoot%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe - See the folders :
%USERPROFILE%/Documents/WindowsPowerShell- or
%USERPROFILE%/OneDrive/Documents/WindowsPowerShell
- PowerShell (7.5.3 for example)
- PowerShell is portable (Linux…)
- Open source: GitHub repo
- Does not come (yet) automatically with Windows. You must install it
- Path to the app:
C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\pwsh.exe - See the folders :
%USERPROFILE%/Documents/PowerShell- or
%USERPROFILE%/OneDrive/Documents/PowerShell
PowerShell (not Windows PowerShell) is the one you should use.
Why should I prefer PowerShell?
| Feature | Windows PowerShell 5.1 | PowerShell 7 |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-platform | ❌ | ✅ Win/Linux/mac |
| Performance | 🐢 | ⚡ Faster (CoreCLR) |
| Support | Finishing | ✅ Fully supported |
| New modules | Rare | 🚀 Continuous updates |
Windows PowerShell is legacy — PowerShell 7 is the future.
Checking the version
$PSVersionTable
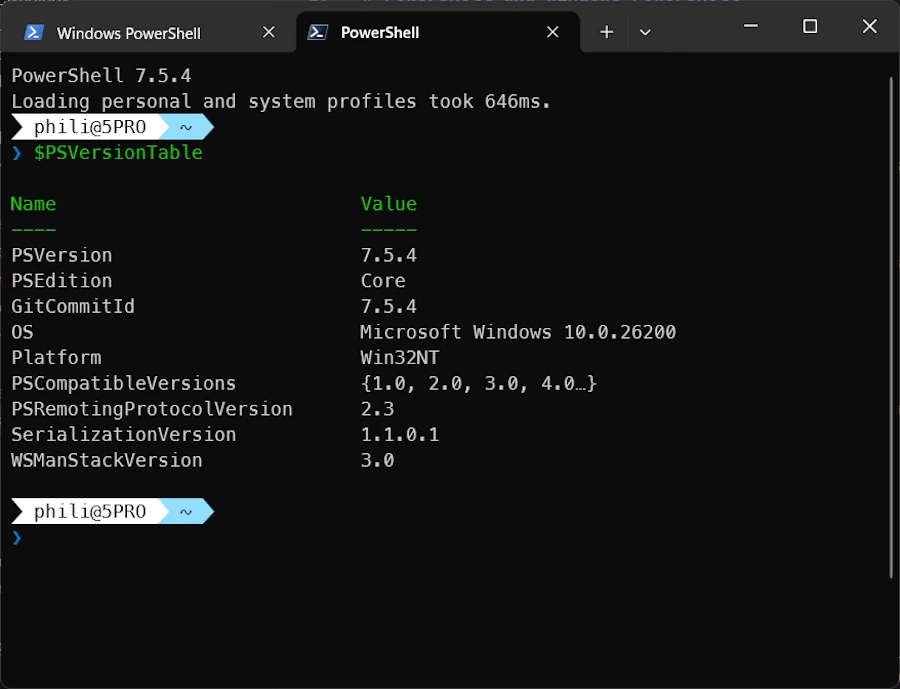
One way to get PowerShell current version with $PSVersionTable
Installing PowerShell
If PowerShell is not yet installed, shame on you 😁. You can however either run one of the 2 commands below:
winget install --id Microsoft.PowerShell --source winget
choco install powershell -y
Once PowerShell is installed
If you want to execute local script run the following command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
Updating PowerShell
Use one of three commands below:
Update-PowerShell
winget upgrade Microsoft.PowerShell
choco upgrade powershell-core
Set PowerShell as your default in Terminal Windows
- Open Terminal Windows (
WIN+X then I) - Settings → Startup → Default profile
- Select PowerShell
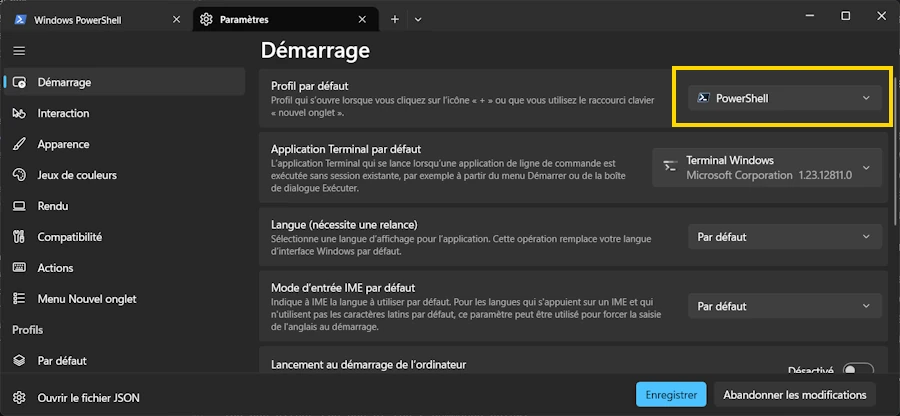
Define PowerShell as your default in Terminal Windows
Configuring PowerShell in VSCode
CTRL,- Look for:
terminal.integrated.defaultProfile.windows - Select:
PowerShell 7
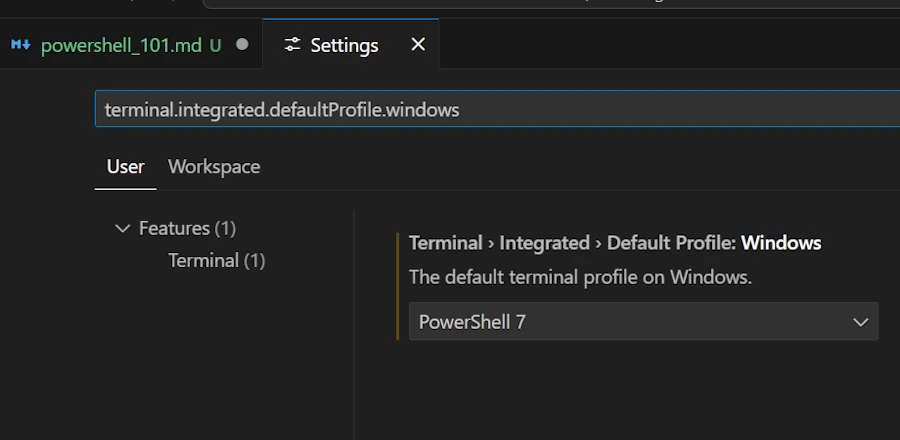
Configuring PowerShell in VSCode
Checking your profile
Open Window Terminal (WIN+X the I)
$PROFILE
C:\Users\phili\OneDrive\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1
C:\Users\phili\OneDrive\Documents\PowerShell\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1
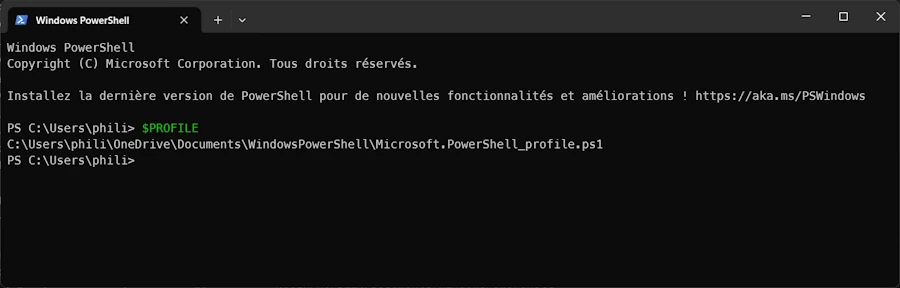
Checking your profile with $PROFILE
About the Profile Files
There are 4 levels of profiles in PowerShell, from the most specific to the most general:
-
$Profile.CurrentUserCurrentHost- File:
Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1 - For: The current user + the specific host (e.g. PowerShell console)
- File:
-
$Profile.CurrentUserAllHosts- File:
profile.ps1 - For: The current user + ALL hosts (console, ISE, VS Code, etc.)
- File:
-
$Profile.AllUsersCurrentHost- File:
Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1(but located in$PSHOME) - For: ALL users on the machine + the specific host
- File:
-
$Profile.AllUsersAllHosts- File:
profile.ps1(but located in$PSHOME) - For: ALL users + ALL hosts
- File:
In practice
- Levels 3 and 4 are in a system folder (like
C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\) and require admin rights. They’re rarely used. - Levels 1 and 2 are in your Documents folder — those are the most common ones.
To see all your profile paths, you can type in PowerShell:
$Profile | Get-Member -MemberType NoteProperty | Select-Object Name
Most people only use one of [1, 2], usually Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1.
About the PowerShell directory
- Keep
Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1.- It runs when you open a standard PowerShell console (including in VS Code).
- Delete
profile.ps1- UNLESS you also use PowerShell ISE or other special hosts
- In practice, 99% of people don’t need it
About the WindowsPowerShell directory
- Do not delete it
- Some scripts or Windows tools may still use PowerShell 5.1.
- You can leave it empty
My ../PowerShell/Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1
oh-my-posh init pwsh --config "$env:POSH_THEMES_PATH/paradox.omp.json" | Invoke-Expression
# Import the Chocolatey Profile that contains the necessary code to enable tab-completions to function for `choco`.
# Be aware that if you are missing these lines from your profile, tab completion for `choco` will not function.
# See https://ch0.co/tab-completion for details.
$ChocolateyProfile = "$env:ChocolateyInstall\helpers\chocolateyProfile.psm1"
if (Test-Path($ChocolateyProfile)) {
Import-Module "$ChocolateyProfile"
}
# I moved from Conda to uv
# This help activate a venv
function venv {
param([string]$EnvName = "venv")
if (Test-Path ".\$EnvName\Scripts\Activate.ps1") {
& ".\$EnvName\Scripts\Activate.ps1"
} elseif (Test-Path "..\$EnvName\Scripts\Activate.ps1") {
& "..\$EnvName\Scripts\Activate.ps1"
} else {
Write-Host "Environment '$EnvName' not found" -ForegroundColor Red
}
}
My ../PowerShell/profile.ps1
# Redirect to the main profile
. "$PSScriptRoot\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1"
FAQ
Does Terminal Windows == PowerShell ?
- No
- Terminal Windows is “just” a modern “host” app.
- PowerShell is the shell that runs inside it.
- Inside Terminal Windows you have Ubuntu, cmd, Windows PowerShell, PowerShell…
What’s the difference between PowerShell and Command Prompt?
Command Prompt (cmd.exe) is the traditional Windows command-line tool. It can run basic commands and batch scripts, but it works mostly with plain text.
PowerShell, on the other hand, is a modern automation and scripting shell based on .NET. It doesn’t just output text — it works with objects, which makes automation, data processing, and tool integration far more powerful.
Cmd is for simple commands. PowerShell is for scripting, automation, and modern system management.
Why does Windows PowerShell still exist?
Windows PowerShell (version 5.1) comes preinstalled with Windows for compatibility. Many enterprise tools and admin scripts created in the past still rely on it.
It stays for legacy support, but development has shifted to PowerShell 7.
Can I uninstall Windows PowerShell?
Not recommended. Some Windows features and management tools still depend on Windows PowerShell 5.1.
You can uninstall it using advanced tools, but it may break parts of Windows. Better approach:
- Set PowerShell 7 as your default
- Keep Windows PowerShell for older scripts
How do I start PowerShell 7? (“pwsh”??)
- After installing PowerShell 7
- In any terminal (Terminal Windows, cmd, Run dialog, etc.)
- You can launch PowerShell by typing:
pwsh
- pwsh is the executable for the modern version of PowerShell.
You can also:
- Search for PowerShell 7 in the Start menu
- Just type the 3 letters
pow. It will be listed
- Just type the 3 letters
- Set PowerShell 7 as your default shell in Terminal Windows settings
Bibliography

Webliography
- PowerShell
- Install PowerShell
- PowerShell GitHub repository
- I know, this playlist is very old BUT I really enjoy the tone of the talk and you can see the father of Powershell… Respect. For what I know he left Microsoft since then.